Battery (auxiliary): In an electric drive
vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides electricity to start the car
before the traction battery is engaged and also powers vehicle
accessories.
Charge port: The charge port allows the vehicle to connect to an external power supply in order to charge the traction battery pack.
DC/DC converter: This device converts
higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the
lower-voltage DC power needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge
the auxiliary battery.
Electric generator: Generates electricity from
the rotating wheels while braking, transferring that energy back to the
traction battery pack. Some vehicles use motor generators that perform
both the drive and regeneration functions.
Electric traction motor: Using power from the
traction battery pack, this motor drives the vehicle's wheels. Some
vehicles use motor generators that perform both the drive and
regeneration functions.
Exhaust system: The exhaust system channels the
exhaust gases from the engine out through the tailpipe. A three-way
catalyst is designed to reduce engine-out emissions within the exhaust
system.
Fuel filler: A nozzle from a high-pressure dispenser attaches to the receptacle on the vehicle to fill the tank.
Fuel tank (gasoline): This tank stores gasoline on board the vehicle until it's needed by the engine.
Internal combustion engine (spark-ignited): In
this configuration, fuel is injected into either the intake manifold or
the combustion chamber, where it is combined with air, and the air/fuel
mixture is ignited by the spark from a spark plug.
Onboard charger: Takes the incoming AC
electricity supplied via the charge port and converts it to DC power for
charging the traction battery. It monitors battery characteristics such
as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge while charging
the pack.
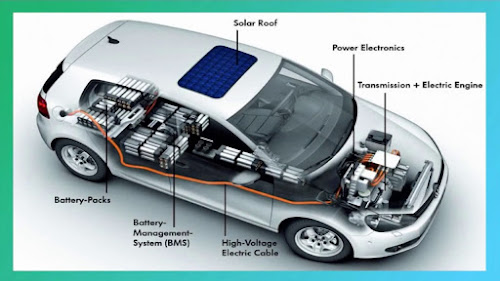
Power electronics controller: This unit manages
the flow of electrical energy delivered by the traction battery,
controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it
produces.
Thermal system (cooling): This system maintains a
proper operating temperature range of the engine, electric motor, power
electronics, and other components.
Traction battery pack: Stores electricity for use by the electric traction motor.
Transmission: The transmission transfers mechanical power from the engine and/or electric traction motor to drive the wheels.
Some Plug-in Hybrid cars on Market:
1. Kia Niro
2.Land Rover P400e
Hybrid-electric Working:
Hybrid electric vehicles are powered by an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, which uses energy stored in batteries.
A hybrid electric vehicle cannot be plugged in to charge the battery.
Instead, the battery is charged through regenerative braking and by the
internal combustion engine. The extra power provided by the electric
motor can potentially allow for a smaller engine. The battery can also
power auxiliary loads and reduce engine idling when stopped. Together,
these features result in better fuel economy without sacrificing
performance.
Key Components of a Hybrid Electric Car
Battery (auxiliary): In an electric drive
vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides electricity to start the car
before the traction battery is engaged and also powers vehicle
accessories.
DC/DC converter: This device converts
higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the
lower-voltage DC power needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge
the auxiliary battery.
Electric generator: Generates electricity from
the rotating wheels while braking, transferring that energy back to the
traction battery pack. Some vehicles use motor generators that perform
both the drive and regeneration functions.
Electric traction motor: Using power from the
traction battery pack, this motor drives the vehicle's wheels. Some
vehicles use motor generators that perform both the drive and
regeneration functions.
Exhaust system: The exhaust system channels the
exhaust gases from the engine out through the tailpipe. A three-way
catalyst is designed to reduce engine-out emissions within the exhaust
system.
Fuel filler: A nozzle from a high-pressure dispenser attaches to the receptacle on the vehicle to fill the tank.
Fuel tank (gasoline): This tank stores gasoline on board the vehicle until it's needed by the engine.
Internal combustion engine (spark-ignited): In
this configuration, fuel is injected into either the intake manifold or
the combustion chamber, where it is combined with air, and the air/fuel
mixture is ignited by the spark from a spark plug.
Power electronics controller: This unit manages
the flow of electrical energy delivered by the traction battery,
controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it
produces.
Thermal system (cooling): This system maintains a
proper operating temperature range of the engine, electric motor, power
electronics, and other components.
Traction battery pack: Stores electricity for use by the electric traction motor.
Transmission: The transmission transfers mechanical power from the engine and/or electric traction motor to drive the wheels.












No comments:
Post a Comment